

.jpg)
Analysis of the size distribution on the nanoparticles released into the air as airborne nanoparticles can be obtained by the EN 17199-4 small rotating drum methodology in which an electronic impactor and a nanoparticle counter are being used. Have questions about testing dynamic light scattering Our engineers are standing by to help you Contact us. The DLS particle size analysis in the liquid phase provides information on the hydrodynamic particle size of the nanoparticles. Nanoparticles down to 3 nanometers can be identified and measured. The upper limit of the technique is in the size range of approximately 10 micrometers and the strong focus of dynamic light scattering is clearly on the nanoparticle size range. The measurement range of the dynamic light scattering technique is therefore also limited on the upper range since larger particles are simply to heavy to display Brownian motion and will also settle too fast. A dynamic light scattering apparatus (10) comprises a laser (12) optically coupled to a light scattering sample (26) via a first monomode optical fibre (18). We also offer unique instruments for electrophoretic light scattering (MP-PALS), differential refractometry and differential viscosity. The faster movement of the smaller particles is due to the energy transfer of liquid molecules to the solid particles and nanoparticles will experience a greater effect of this energy transfer than larger and heavier particles. Our dynamic light scattering (DLS) products operate in traditional cuvette as well as on-line and automated, high-throughput modes. sounds in the garden at night, turned on a light and discovered a large Norway rat hanging on our bird feeder enjoying a meal.
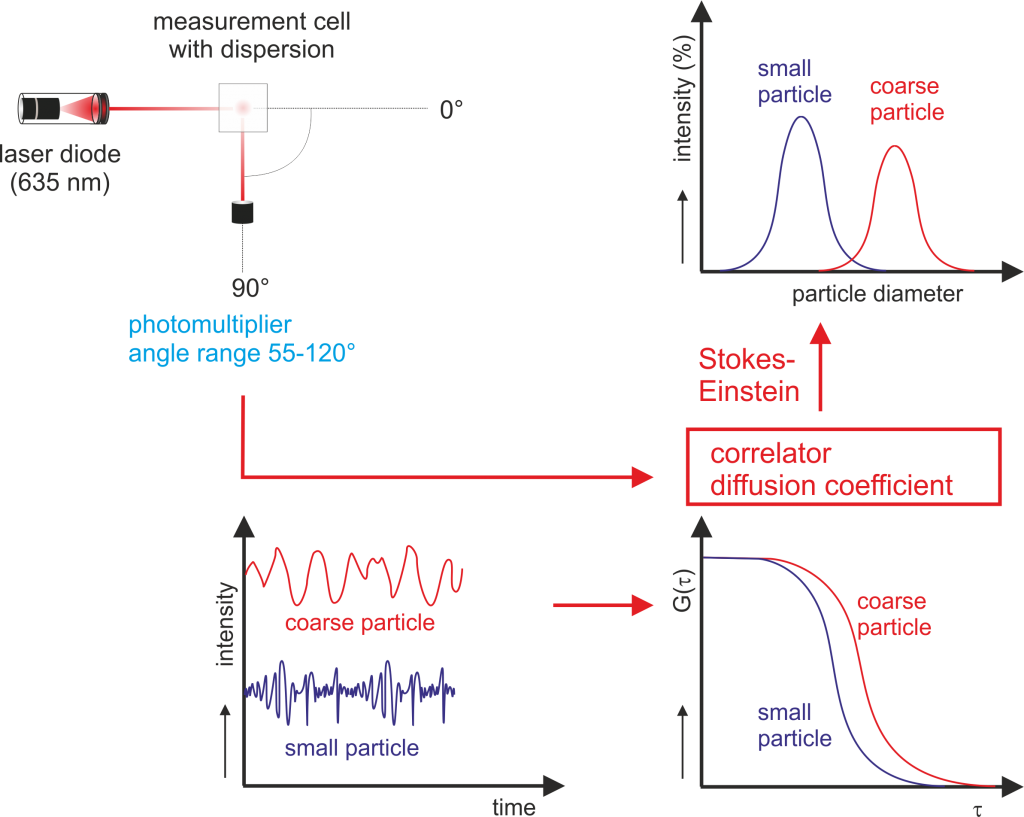
The Brownian motion of particles in the liquid phase occurs randomly in every direction and smaller particles will typically travel faster than larger particles. The technique uses a laser to track the Brownian motion of particles and in particular nanoparticles. DLS is the measurement of light interference based on the Brownian motion of nanoparticles in suspension and a correlation of its velocity (diffusion coefficient) with its size using StokesEinstein equation ( Bizheva et al. Analysis of the nanoparticle size distribution and nanoparticles identification can be obtained by means of Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS), sometimes also referred to as Photon Correlation Spectroscopy. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) is the most common approach to analyze hydrodynamic particle size and distribution of the particles over a range of sizes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
